Robots have transcended the realm of science fiction, becoming a tangible, if not ubiquitous, feature of the modern world. From streamlining manufacturing processes to assisting healthcare professionals, robots are catalysts for efficiency and innovation.
But just how diverse is the landscape of robots? This post will provide a comprehensive look at how many types of robots are there?, their defining characteristics, and their impact on society.
Classification of Robots

1. Industrial Robots
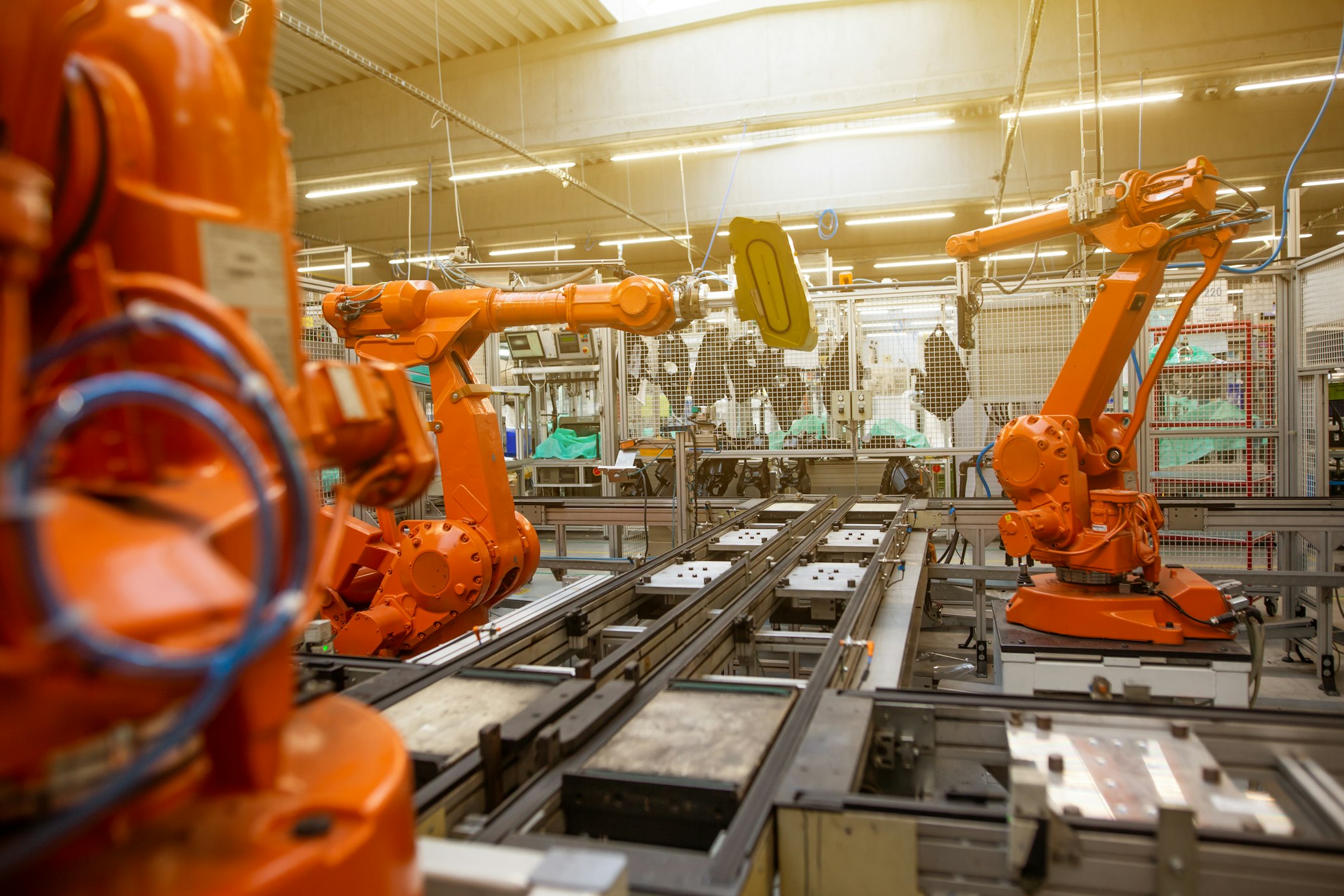

The Workhorses of Manufacturing
Industrial robots are the bedrock of modern manufacturing, performing repetitive tasks with unnerving precision and efficiency. These robots are often seen in controlled environments, such as assembly lines and production plants.
They handle tasks ranging from welding and painting to packaging and palletizing. Over time, they have evolved to be more flexible and autonomous, but their primary focus remains on the execution of physical tasks.
You may line: What Is Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Its Role in AI
Examples:
- Robotic arms that assemble electronics
- Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) in warehouses
- 3D printing robots in additive manufacturing processes
2. Service Robots
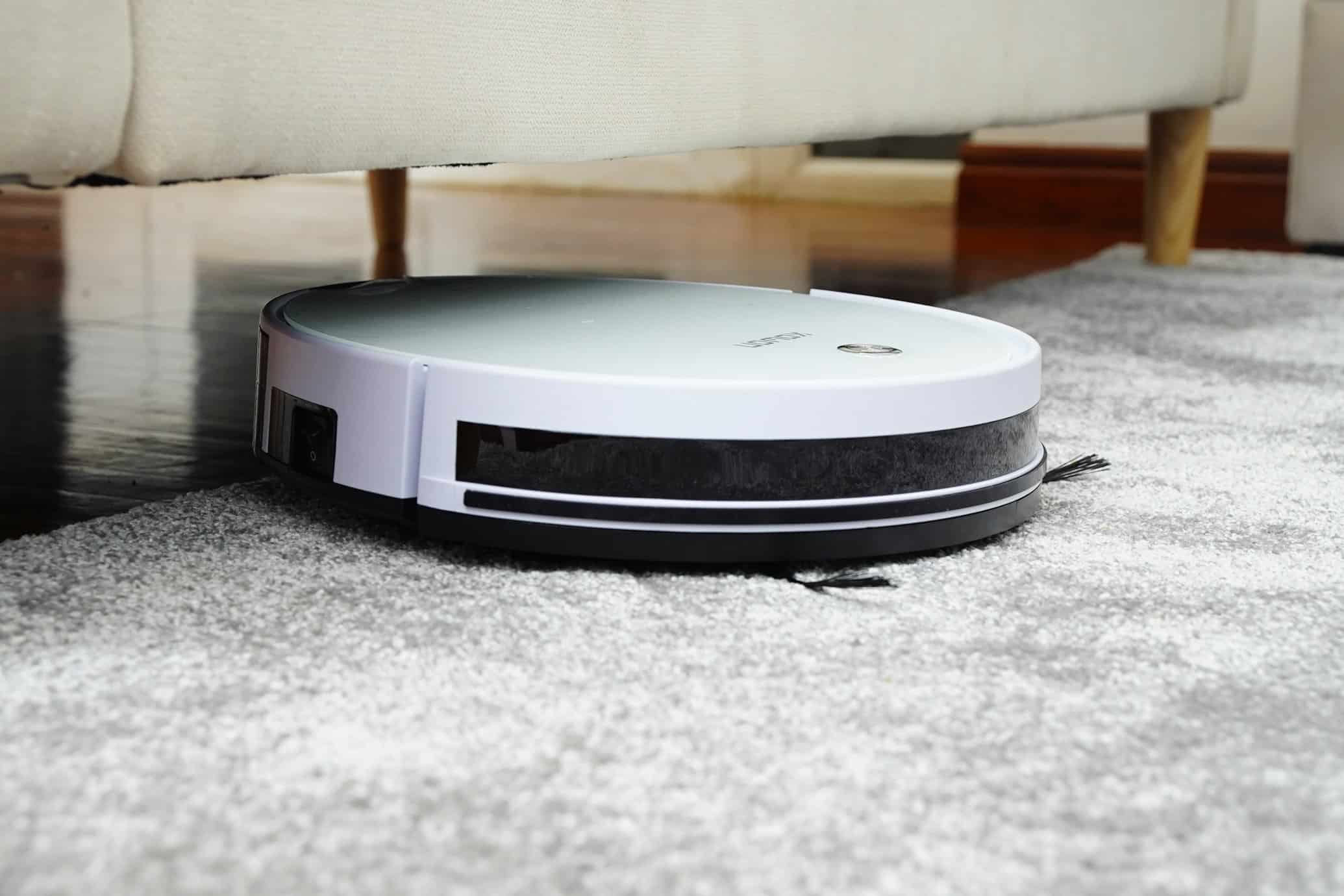

The Helpers in Human Settings
Service robots are designed to serve humans, either autonomously or under direct human control. Unlike industrial robots, service robots operate in less structured environments and are frequently used for hazardous, dull, or dirty work.
They are also an integral part of tackling societal challenges, such as an aging population and the healthcare demands it entails.
Examples:
- Medical robots assisting in surgery
- Domestic robots undertaking household chores
- Agriculture robots for planting and harvesting crops
4. Collaborative Robots
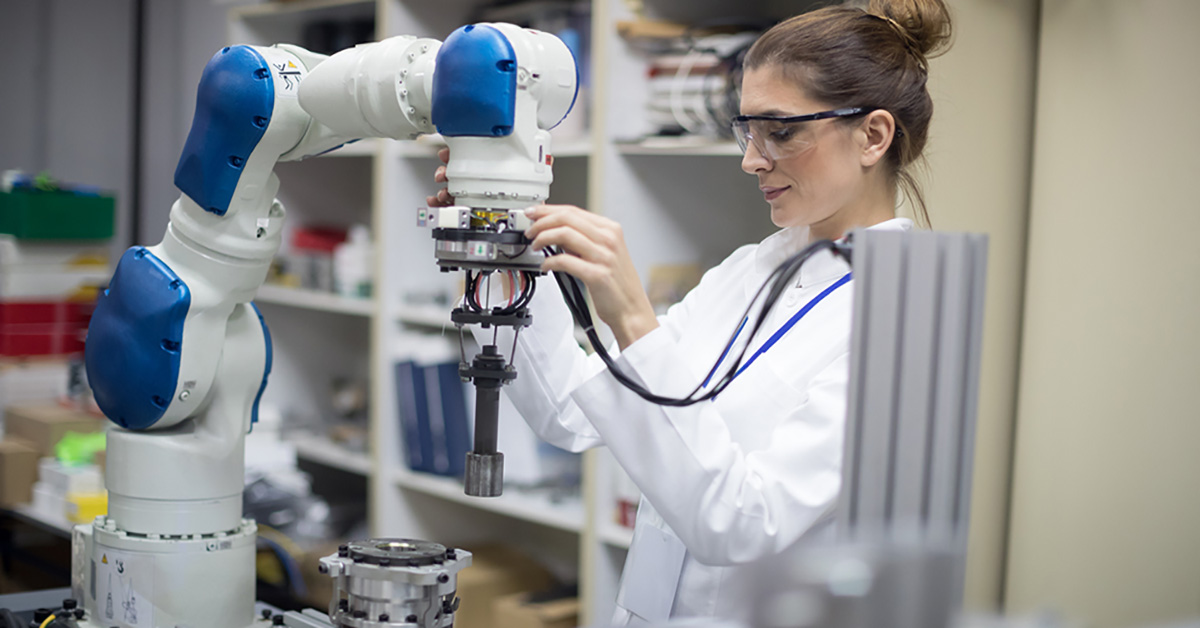

Merging man with machine
Collaborative robots, or “cobots,” are a newer breed of robot designed to physically interact and work alongside humans in a shared space. These robots are crafted with safety features and agility in mind, allowing for close collaboration without the need for traditional safety barriers.
Examples:
- Cobots assist workers in on-site construction.
- In-vehicle assembly robots that collaborate with car manufacturers
5. Social Robots

The Heart and Face of Robotics
Social robots are a unique category that focuses on interaction with humans. They are meant to simulate and potentially elicit emotional responses while also carrying out specific tasks.
Although still in the early stages of development, social robots have immense potential for fields like therapy, education, and even companionship.
You may line: Artificial Intelligence in Education: Opportunities and Challenges
Examples:
- Paro, the therapeutic robotic seal
- Robotics for autism therapy
- Educational robots for interactive learning
6. Autonomous Vehicles

Robotics on the Move
Autonomous vehicles, or AVs, are robots designed for transportation. They are capable of navigating and functioning without human intervention.
Emerging technologies like self-driving cars and drones fall under this category, representing a significant leap toward the automation of transportation.
Examples:
- Self-driving cars for personal and public transportation
- Drones for aerial surveillance and delivery services
- Underwater robots for marine exploration
7. Military Robots

Precision and power in combat
Military robots are used by the armed forces for a variety of purposes, including reconnaissance, bomb disposal, and combat operations. These robots are designed to operate in high-risk scenarios, reducing the exposure of human soldiers to danger.
Examples:
- Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)
- Bomb disposal robots
- Robotic exoskeletons for enhanced soldier performance and support
The Technology Behind Each Type

AI and Machine Learning
The backbone of modern robotics, AI and machine learning, enable robots to learn from experience, adapt to new information, and perform complex tasks.
These technologies empower robots with capabilities that were once reserved for the human brain, allowing them to make decisions in real-time and operate more autonomously.
Sensor Technology
Robots rely on sensors to perceive and interact with their environment. From cameras and lidars that provide visual data to haptics and proprioceptive sensors that lend a sense of touch and position, sensor technology is crucial in determining a robot’s operability and safety.
Application Areas and Real-World Examples

Healthcare and Medical
Robots have made significant inroads in healthcare, assisting surgeons in delicate operations, providing physical therapy, and even dispensing medication. These units use advanced medical PCB for a reliable control system on top of the sensors and software installations. They are instrumental in enhancing precision, reducing infection rates, and alleviating the strain on medical personnel.
Space Exploration
Robots have been pivotal in humanity’s quest to explore the cosmos, performing tasks on distant planets that are impractical or dangerous for humans. Rovers and landers have revealed the secrets of Mars, while probes and telescopes are extending our vision across the universe.
Home and Personal Use
Domestic robots are poised to transform the way we manage the mundane tasks of daily life. From robotic vacuum cleaners and lawnmowers to personal assistants, these robots are entering homes and lifestyles, catering to personal needs and freeing up time for more meaningful pursuits.
Future Trends and Challenges

The Rise of AI-Enhanced Robotics
The robotics field encompasses various types of robots, ranging from industrial robots to social robots and more. Each type serves specific functions and applications, contributing to the diverse landscape of robotics technology.
Ethical Considerations
The increasing presence of robots in our lives raises profound ethical questions, such as the impact on employment, the proliferation of autonomous weapons, and the rights and treatment of AI with the semblance of sentient beings.
Preparing for Robotic Integration
Society must adapt to and prepare for the integration of robots into everyday life. This includes changes in education and workforce training, infrastructure development to support robotic operations, and the establishment of regulatory frameworks to ensure responsible use.
Conclusion: The Diverse and Exciting World of Robots
In conclusion, the question “How Many Types of Robots Are There?” reveals the complexity and breadth of the robotics field. From service robots that simplify daily tasks to collaborative and social robots that work alongside humans, the diversity underscores the technology’s vast potential.
Autonomous vehicles and military robotics showcase the advancements in mobility and precision, while the underlying AI and sensor technology drive their capabilities further.
As we look to the future, the continued evolution of robotics promises to reshape our world, presenting both opportunities and challenges that will require thoughtful consideration and adaptation.
The myriad types of robots not only highlight the progress in engineering and science but also reflect our ambitions and creativity in pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.